Cloud adoption continues to accelerate across industries, but as organizations move more workloads into Amazon Web Services (AWS), one challenge consistently arises: managing and allocating costs effectively. Without visibility and accountability, cloud spend can spiral out of control, leaving finance teams frustrated and business units unable to see the value of their investments.
That’s where AWS cost allocation comes in. By leveraging AWS’s built-in tools and best practices, you can assign cloud costs to the right owners, improve financial transparency, and align your cloud usage with business outcomes. And if you want expert guidance, TruCost.Cloud specializes in helping companies design, implement, and optimize cost allocation models that fit both technical and financial needs.
What is AWS Cost Allocation?
Cost allocation is the process of identifying, categorizing, and assigning the costs of cloud resources to specific users, teams, projects, or business units. In simple terms, it ensures that the right part of your organization takes ownership of the costs it generates.
Cost allocation can serve two main purposes:
- Showback – providing visibility of costs to the right stakeholders without enforcing financial charges.
- Chargeback – formally assigning and recording costs in the organization’s general ledger to hold business units financially accountable.
AWS offers several native capabilities—such as accounts, tags, cost categories, and billing tools—to help businesses adopt either showback or chargeback models effectively. TruCost.Cloud builds on these capabilities by aligning them with your FinOps framework, ensuring cost accountability drives both savings and business value.
Why Cost Allocation Matters
Before diving into the tools, it’s important to understand why AWS cost allocation is critical:
1. Accountability – Teams are more mindful of costs when they can see and own them.
2. Financial Accuracy – Helps finance departments integrate cloud costs into standard accounting systems.
3. Cost Optimization – Clear visibility enables identification of waste, underutilized resources, and opportunities for savings.
4. Business Value Tracking – Links cloud investments back to specific business outcomes, making it easier to justify spend.
At TruCost.Cloud, we’ve seen businesses reduce AWS spend by 20–40% once they implement structured cost allocation and governance practices.
Key Dimensions for Cost Allocation
Every business has unique needs, but most organizations allocate costs across similar dimensions:
- Business Unit / Division
- Cost Center
- Department / Team
- Project / Application
- Environment (Production, Staging, Development)
- Architectural Component (Database, Networking, Storage, etc.)
Once these dimensions are defined, they can be mapped to your AWS workloads and resources. TruCost.Cloud helps customers define these dimensions in practical ways that scale as cloud usage grows.
AWS Cost Allocation Strategies
AWS provides flexibility in how you organize and allocate costs. Let’s look at the most common approaches.
1. Cost Accountability by AWS Account
AWS accounts are the fundamental building block for both security and billing. All usage and charges are tied to a specific account, making account-level allocation the most straightforward option.
Example: Suppose your company has three departments—Marketing, Finance, and Product Development. You can give each department its own AWS account under a single AWS Organization. This setup allows:
- Direct visibility into costs via AWS Cost Explorer.
- Simplified chargeback using account-level invoices.
- Easy reporting with saved views in Cost Explorer.
For small businesses, separate invoices per account work well. For enterprises, consolidated billing provides a single invoice with per-account breakdowns—perfect for internal chargeback.
2. Cost Accountability by Groups of Accounts
When a business unit owns multiple AWS accounts, grouping accounts is often more practical.
With AWS Cost Categories and Invoice Configuration, you can apply metadata to accounts, group them logically, and receive consolidated invoices for each group.
TruCost.Cloud helps clients configure these invoice groups so finance teams get exactly the level of granularity they need—without drowning in unnecessary detail.
3. Cost Accountability by Resources Within Accounts
Not all accounts belong to a single owner. For example, an Infrastructure team may run multiple workloads in one account.
AWS Cost Allocation Tags provide resource-level granularity. Tags can indicate ownership (Owner=TeamA, Project=CRM) and can be combined with Cost Categories for simplified reporting.
TruCost.Cloud often helps customers design and enforce tagging strategies with automation, ensuring every resource is properly tagged from day one.
4. Cost Accountability for Shared Resources
Shared services—like container platforms (ECS, EKS) or networking—require more advanced approaches.
Options include:
- Cellular Architecture – breaking platforms into smaller units.
- Split Cost Allocation Data – container-level cost breakdowns in the Cost and Usage Report.
- Split Charge Rules – distributing unallocated shared costs proportionally.
This avoids disputes and ensures shared services don’t become “shadow IT” with no clear financial owner. TruCost.Cloud guides customers in implementing proportional allocation policies that finance and engineering teams both trust.
Handling Commitment-Based Pricing (RIs and Savings Plans)
Commitment-based pricing like Savings Plans (SPs) and Reserved Instances (RIs) bring significant discounts—but also complexity.
Two strategies stand out:
1. Amortized Allocation – spreading upfront commitment costs over time with Cost Explorer’s Amortized views.
2. Custom Allocation – using AWS Billing Conductor to define internal rules, ensuring commitments and discounts are distributed fairly across teams.
At TruCost.Cloud, we often see clients struggling here. Our FinOps experts help define fair commitment-sharing policies, ensuring finance teams avoid disputes while maximizing AWS discounts.
Best Practices for AWS Cost Allocation
Here are some proven practices from AWS and TruCost.Cloud customer engagements:
1.Start with accounts – Simple, scalable, and clear.
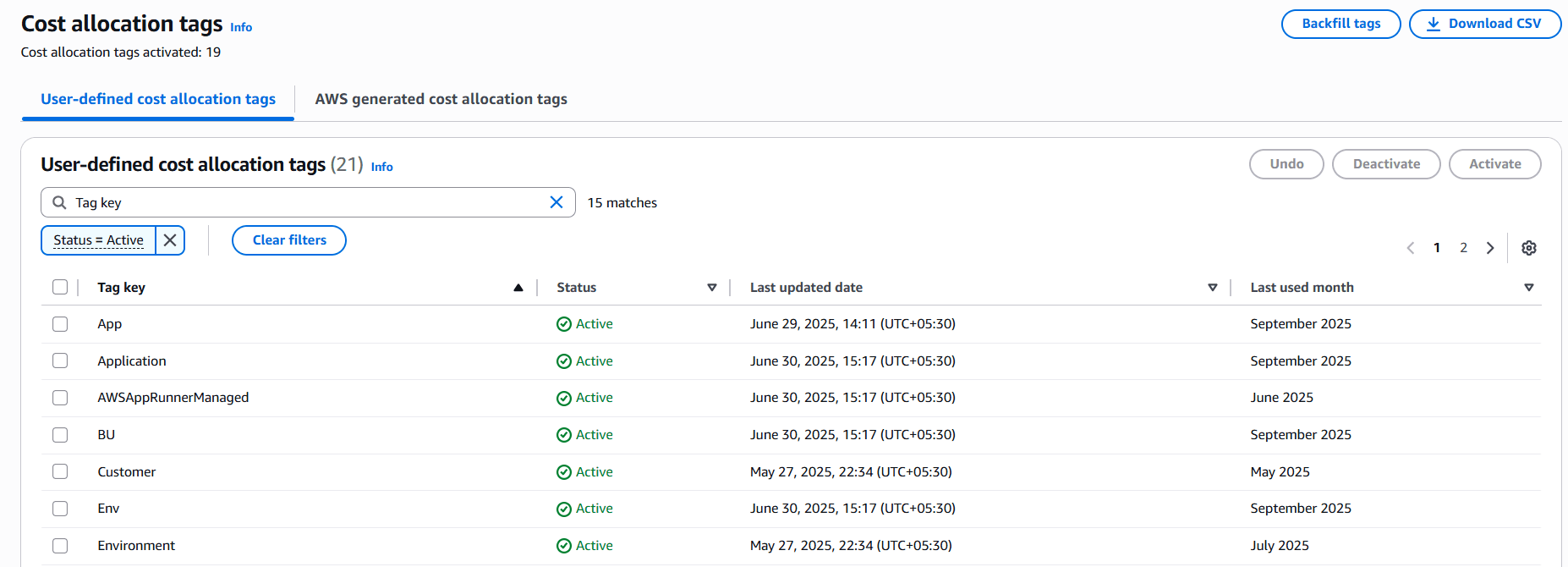
2. Define a tagging standard – Use required tags like Owner, Project, and Environment.
3. Use Cost Categories – Reduce dependency on perfect tagging.
4. Automate reporting – Schedule reports and dashboards with AWS Data Exports.
5. Review quarterly – Cloud usage evolves fast; so should your allocation model.
6. Align with finance – Ensure your cost allocation ties directly into budgets and forecasts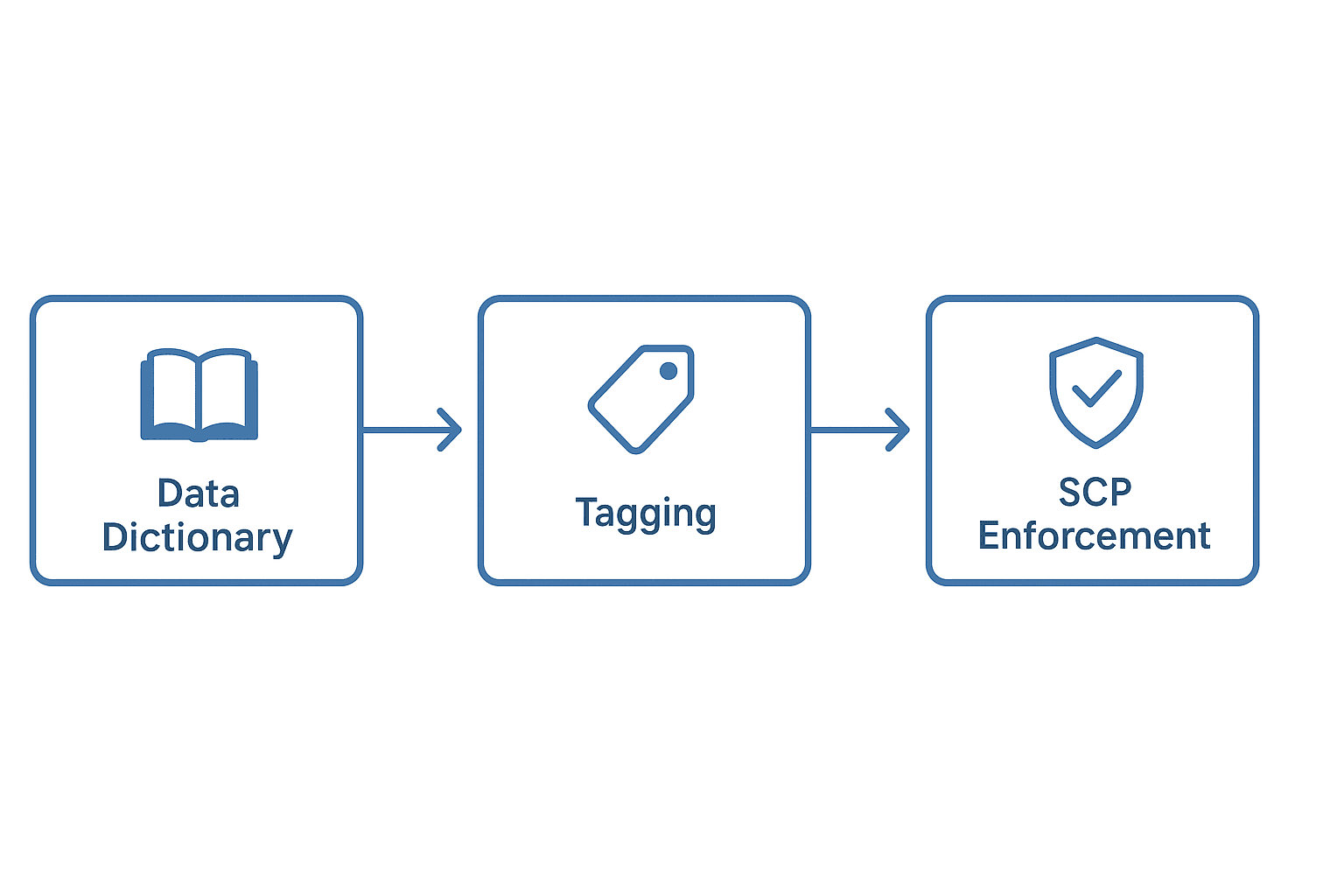
Mastering AWS Resource Tagging: The Power of Data Dictionaries and SCP Policies
In today’s dynamic cloud environment, managing costs, governance, and compliance effectively is a priority for every organization. A critical component of achieving this is resource tagging—the practice of assigning metadata (tags) to AWS resources. However, without proper planning and governance, tagging can quickly become inconsistent, incomplete, or even misleading.
This is where data dictionaries and Service Control Policies (SCPs) come into play. Together, they ensure a structured, consistent, and enforceable approach to tagging.
Understanding AWS Resource Tagging
AWS tags are key-value pairs attached to resources such as EC2 instances, S3 buckets, RDS databases, and Lambda functions. They serve multiple purposes:
- Cost allocation: Assign costs to business units, projects, or teams.
- Operational management: Identify and manage resources efficiently.
- Compliance and security: Ensure resources meet organizational policies.
For example, a tag might look like:
Key: Environment
Value: Production
While tagging seems straightforward, organizations often encounter these challenges:
- Inconsistent naming: “Prod” vs “Production.”
- Missing tags: Resources without tags cannot be accounted for in reports.
- Incorrect tagging: Wrong project, team, or environment assigned.
This is why a data dictionary and SCP-based enforcement are critical.
What is a Resource Tagging Data Dictionary?
A data dictionary is a centralized repository that defines all allowed tags, their keys, allowed values, descriptions, and applicable resources. It serves as the blueprint for a consistent cloud tagging strategy.
Key Components of a Tagging Data Dictionary:
Component | Description |
Tag Key | The name of the tag (e.g., Environment, Project, Owner) |
Allowed Values | Predefined values for each key (e.g., Environment: Production, Staging, Development) |
Description | Explanation of the tag’s purpose |
Resource Scope | Which resources the tag applies to (e.g., EC2, S3, Lambda) |
Mandatory/Optional | Indicates whether the tag must be applied to a resource |
A well-maintained data dictionary ensures consistency, clarity, and accountability. Teams know exactly which tags to use and what values are allowed.
Enforcing Tagging with Service Control Policies (SCPs)
Even with a data dictionary, human error or lack of governance can lead to incorrect tagging. AWS Service Control Policies (SCPs) are a solution. SCPs are policies applied at the AWS Organization level that define what actions accounts or users are allowed (or denied) to perform.
By leveraging SCPs, you can:
- Prevent creation of untagged resources.
- Enforce adherence to approved tag values.
- Ensure compliance with governance rules.
Example: SCP to Enforce Mandatory Tags
Here’s an example SCP that ensures all EC2 instances must have the “Environment” tag:
{
“Version”: “2012-10-17”,
“Statement”: [
{
“Sid”: “DenyCreateEC2WithoutEnvironmentTag”,
“Effect”: “Deny”,
“Action”: “ec2:RunInstances”,
“Resource”: “*”,
“Condition”: {
“StringNotEquals”: {
“aws:RequestTag/Environment”: [“Production”, “Staging”, “Development”]
}
}
}
]
}
This policy denies the creation of EC2 instances if the Environment tag is missing or invalid, ensuring compliance with your data dictionary.
Benefits of Combining Data Dictionaries with SCPs
1. Consistency Across the Organization
All teams follow the same tagging rules, avoiding confusion and errors.
2. Simplified Cost Allocation
Accurate tags make it easy to generate reports and allocate costs correctly.
3. Improved Governance and Security
Enforcing mandatory tags ensures resources are traceable and managed properly.
4. Operational Efficiency
Teams can quickly identify resources, reducing troubleshooting time and manual audits.
At TruCost.Cloud, we help organizations implement structured tagging strategies that combine data dictionaries with SCP enforcement, ensuring your AWS environment is cost-efficient, compliant, and fully auditable.
Best Practices for Tagging Governance
- Start with a Tagging Strategy: Define the purpose of each tag and its scope.
- Build a Comprehensive Data Dictionary: Include all mandatory and optional tags.
- Use SCPs for Enforcement: Prevent incorrect or missing tags proactively.
- Automate Audits: Use AWS Config or Lambda scripts to continuously monitor tagging compliance.
- Educate Teams: Make sure every team understands the tagging rules and their importance.
Conclusion
Effective AWS cost allocation and resource tagging are the cornerstones of cloud financial management (CFM) and FinOps. While cost allocation ensures accountability, transparency, and business value, proper resource tagging provides visibility, governance, and operational efficiency.
Whether you’re aligning costs by accounts, tagging resources for granularity, or implementing advanced allocation with Billing Conductor, the principles remain the same:
- Start simple.
- Scale with business needs.
- Review and refine regularly.
By creating a comprehensive resource tagging data dictionary and enforcing it through Service Control Policies (SCPs), organizations can achieve consistency, reduce errors, and strengthen cloud governance.
At TruCost.Cloud, we help organizations design, implement, and scale cost allocation and tagging frameworks that not only reduce spend but also foster a culture of accountability across engineering and finance. With the right cost allocation model, proper tagging practices, and a trusted partner, you can maximize AWS savings, build financial trust, and drive measurable business value from every cloud dollar spent.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About AWS Cost Allocation
Q1. What is AWS cost allocation, and why is it important?
AWS cost allocation is the process of assigning cloud expenses to the right users, teams, or business units. It ensures accountability, financial accuracy, and helps identify savings opportunities. Without cost allocation, organizations risk overspending and lack visibility into where money is going.
Q2. What’s the difference between showback and chargeback in AWS?
- Showback: Provides visibility of costs to business units without enforcing financial charges.
- Chargeback: Formally assigns costs to business units in the general ledger for accountability.
Both models are supported by AWS through accounts, tags, cost categories, and Billing Conductor.
Q3. How do I allocate AWS costs to different teams or projects?
You can allocate AWS costs using:
- Separate AWS accounts for each team or department.
- Cost allocation tags to track ownership at the resource level.
- AWS Cost Categories to group costs by project, application, or environment.
- Billing Conductor for custom internal billing models.
Q4. How does TruCost.Cloud help with AWS cost allocation?
TruCost.Cloud specializes in FinOps practices. We help businesses:
- Define allocation dimensions (teams, projects, environments).
- Automate tagging and enforce governance.
- Design fair allocation rules for shared resources and commitments.
- Optimize costs while improving financial transparency.
Our customers often see 20–40% AWS cost savings after structured allocation.
Q5. Can AWS cost allocation help with savings plans and reserved instances?
Yes. Commitment-based pricing like Savings Plans (SPs) and Reserved Instances (RIs) often cause disputes if not shared fairly. Using amortized allocation in Cost Explorer or custom allocation with AWS Billing Conductor, organizations can distribute discounts across teams transparently.
Q6. What are the best practices for AWS cost allocation?
- Start with account-level allocation for clarity.
- Standardize mandatory tags like Owner, Project, and Environment.
- Use Cost Categories to simplify reporting.
- Automate reporting with AWS Data Exports.
- Review allocation policies quarterly to adapt to evolving workloads.
Q7. What happens if my AWS resources are not tagged properly?
If resources aren’t tagged, costs become unallocated and hard to track. This leads to “orphaned spend” where no team takes ownership. TruCost.Cloud helps customers implement tagging automation and governance so every resource is accounted for.
Q8. Is AWS cost allocation only for large enterprises?
No. Cost allocation benefits startups, SMBs, and enterprises alike. Small businesses gain visibility without complex overhead, while enterprises rely on allocation models for financial governance and compliance. TruCost.Cloud tailors solutions based on company size and maturity.
Q9. How often should I review my AWS cost allocation model?
At least quarterly. Cloud usage evolves quickly, and allocation models should reflect changes in teams, workloads, and budgets. TruCost.Cloud recommends regular FinOps reviews to stay aligned with business growth.
Q10. How do I get started with AWS cost allocation?
- Define business dimensions (teams, projects, environments).
- Organize workloads using accounts and tags.
- Use Cost Explorer, Cost Categories, and Billing Conductor for reporting.
- Engage a FinOps partner like TruCost.Cloud for expert guidance and automation.
11. What is AWS resource tagging and why is it important?
AWS resource tagging is the practice of assigning key-value metadata pairs to AWS resources such as EC2 instances, S3 buckets, and RDS databases. Tagging is important because it enables cost allocation, operational management, compliance, security tracking, and improved resource visibility across your cloud environment.
12. What is a resource tagging data dictionary in AWS?
A resource tagging data dictionary is a centralized repository that defines all allowed tags, their keys, acceptable values, descriptions, and applicable resources. It acts as a “rulebook” for consistent tagging, ensuring teams apply tags correctly, reducing errors, and supporting governance.
13. How do AWS Service Control Policies (SCPs) enforce tagging compliance?
SCPs are policies applied at the AWS Organization level that control what actions accounts or users can perform. By using SCPs, organizations can prevent the creation of untagged resources, enforce mandatory tag values, and ensure adherence to governance standards defined in the data dictionary.
14. What are the best practices for AWS resource tagging?
- Define a clear tagging strategy aligned with cost allocation and operational goals.
- Maintain a comprehensive data dictionary including mandatory and optional tags.
- Use SCPs to enforce tagging compliance.
- Automate audits with AWS Config or Lambda to monitor compliance.
- Educate teams on tagging standards to ensure consistency.
15. Which AWS resources can be tagged?
Most AWS resources support tagging, including EC2 instances, S3 buckets, RDS databases, Lambda functions, VPCs, IAM roles, and CloudFormation stacks. Tagging support may vary by service, so always check AWS documentation for each resource type.
16. Can tagging help with AWS cost allocation?
Yes. Tags allow organizations to categorize costs by business unit, project, environment, or team. Properly applied tags ensure accurate cost reports, facilitate chargebacks, and simplify FinOps processes.
17. What happens if resources are not tagged correctly?
Incorrect or missing tags can lead to inaccurate cost reporting, governance gaps, compliance risks, and operational inefficiencies. Teams may struggle to identify resources, allocate costs properly, or enforce security policies effectively.
18. How do I enforce mandatory tags using AWS SCPs?
You can write SCPs that deny resource creation or modification if required tags are missing or invalid. For example, an SCP can prevent creating EC2 instances without the “Environment” tag, ensuring compliance with your tagging data dictionary.
19. What tools can help monitor tagging compliance in AWS?
- AWS Config: Monitors resource compliance against tagging rules.
- AWS Lambda: Automates audits and remediation for incorrect or missing tags.
- AWS CloudTrail: Tracks tag changes and helps identify unauthorized modifications.
20. Why combine data dictionaries and SCPs for tagging governance?
Data dictionaries ensure consistent tagging standards, while SCPs enforce compliance at the organizational level. Together, they prevent errors, improve cost allocation, enhance security, and streamline operational management.