Introduction
In the cloud-driven era, data is the lifeblood of every organization. From startups to global enterprises, companies generate, process, and store vast amounts of data daily. Managing this data efficiently—while ensuring scalability, durability, and cost optimization—can be challenging.
That’s where Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) steps in.
Launched in 2006, Amazon S3 is one of AWS’s foundational services, offering secure, scalable, and durable object storage for any amount of data. Whether you’re hosting static websites, storing backups, or powering big data analytics, S3 provides the backbone for reliable data management in the cloud.
What is Amazon S3?
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) is an object storage service that allows you to store and retrieve any amount of data at any time, from anywhere on the web. It’s designed for 99.999999999% (11 nines) durability and 99.99% availability over a given year.
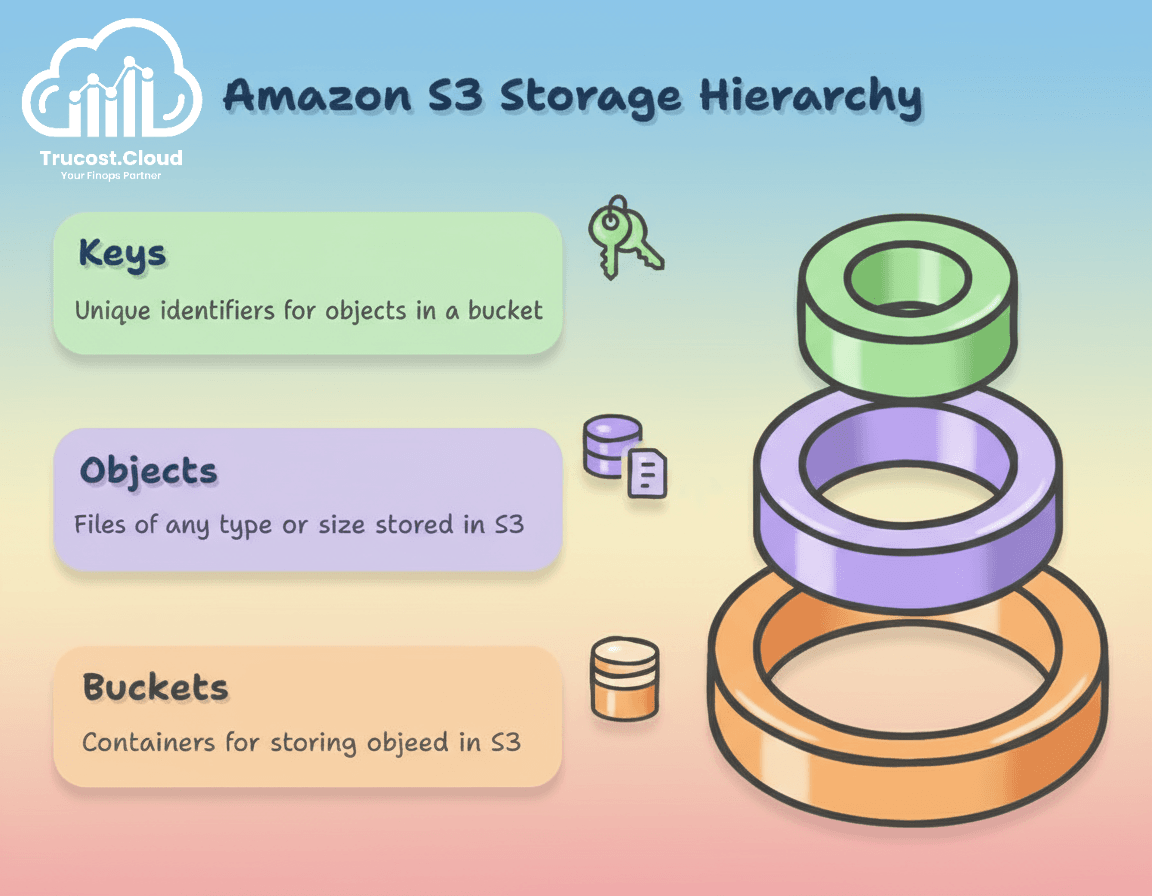
Unlike traditional file or block storage, S3 stores data as objects within buckets:
- Objects: Data is stored as “objects,” which include the file itself (of any type or size) along with its associated metadata that describes the file. Each object can be up to 5 TB in size.
- Buckets: are containers of objects. To store data in Amazon S3, you first need to create a bucket, assign it a unique name, and choose an AWS Region where it will reside. Then, the data is uploaded as objects in the Amazon S3 bucket.
- Keys: Every object within a bucket is assigned a unique “key,” which acts like the object’s filename or path.
Why Use Amazon S3?
Amazon S3 has become the go-to storage solution for businesses for several reasons:
1. Infinite Scalability
Storage capacity scales automatically, so you never have to worry about running out of space. S3 automatically scales to handle petabytes or even exabytes of data without manual provisioning.
2. High Durability & Availability
Amazon S3 is designed for maximum durability and availability by automatically storing your data across multiple devices and facilities within a region.
- Durability: S3 provides 11 nines (99.999999999%) durability for all objects, meaning your data is extremely resilient to hardware failures. This applies to all S3 storage classes.
- Availability: S3 offers high availability, with 99.99% uptime for S3 Standard and slightly lower availability for other storage classes like S3 One Zone-IA.
Even if one facility or device fails, your data remains safe and accessible. This makes S3 a reliable choice for both everyday storage and mission-critical applications.
3. Cost Efficiency
With pay-as-you-go pricing and multiple storage classes, you only pay for what you use. You can optimize costs further with lifecycle policies that move infrequent accessed data to cheaper tiers automatically.
4. Security & Compliance
Amazon S3 provides enterprise-grade security features to protect your data:
- Encryption – Supports server-side encryption (SSE-S3, SSE-KMS, SSE-C) and client-side encryption to safeguard data at rest and in transit.
- Access Control – Fine-grained control using Access Control Lists (ACLs) and Bucket Policies.
- Identity & Access Management (IAM) – Manage access using IAM roles and policies.
- Integration with AWS KMS – Centralized key management and auditing for encrypted data.
Amazon S3 also complies with major industry and regulatory standards, making it suitable for sensitive and regulated workloads:
- PCI-DSS – For secure payment card data storage.
- HIPAA – For storing protected health information.
- FedRAMP – For government cloud security requirements.
- GDPR – Supports compliance with the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation for personal data protection.
5. Integration with AWS Ecosystem
S3 integrates seamlessly with AWS services like:
- Amazon Athena for querying data directly
- AWS Glue for ETL
- Amazon Redshift for analytics
- Amazon CloudFront for content delivery
- AWS Backup, SageMaker, and more
6. Performance and Global Reach
Amazon S3 delivers high throughput and low latency, making it suitable for performance-sensitive applications. With multiple AWS regions and integration with Amazon CloudFront edge locations, S3 enables fast, reliable access to data for users around the globe, making it ideal for global applications and content distribution.
How Amazon S3 Works
Amazon S3 follows a simple structure but operates at massive scale. Let’s break it down:
1. Buckets
A bucket is the top-level container that holds your data (objects).
Each bucket has:
- A unique name (globally across AWS)
- A region (data is stored in that AWS Region)
- Access permissions (who can read/write)
- Versioning, logging, and lifecycle rules
2. Objects
An object consists of:
- Data: The file itself (image, video, text, etc.)
- Metadata: Key-value pairs describing the object (e.g., content type, creation date)
- Key: The unique identifier (like a file path)
3. Accessing Data
You can access S3 data via:
- AWS Management Console
- AWS CLI (Command Line Interface)
- SDKs / APIs for programmatic access
- Pre-signed URLs for temporary secure sharing
4. Versioning
S3 supports versioning, allowing you to maintain multiple variants of an object.
This helps prevent accidental overwrites or deletions—ideal for data protection and backup scenarios.
5. Replication
You can replicate data across regions using:
- Cross-Region Replication (CRR)
- Same-Region Replication (SRR)
This enhances redundancy and supports compliance or latency requirements.
Amazon S3 Storage Classes (Types)
Amazon S3 provides a variety of storage classes, each optimized for specific use cases and data access patterns. Choosing the right one is key to optimizing cost and performance.
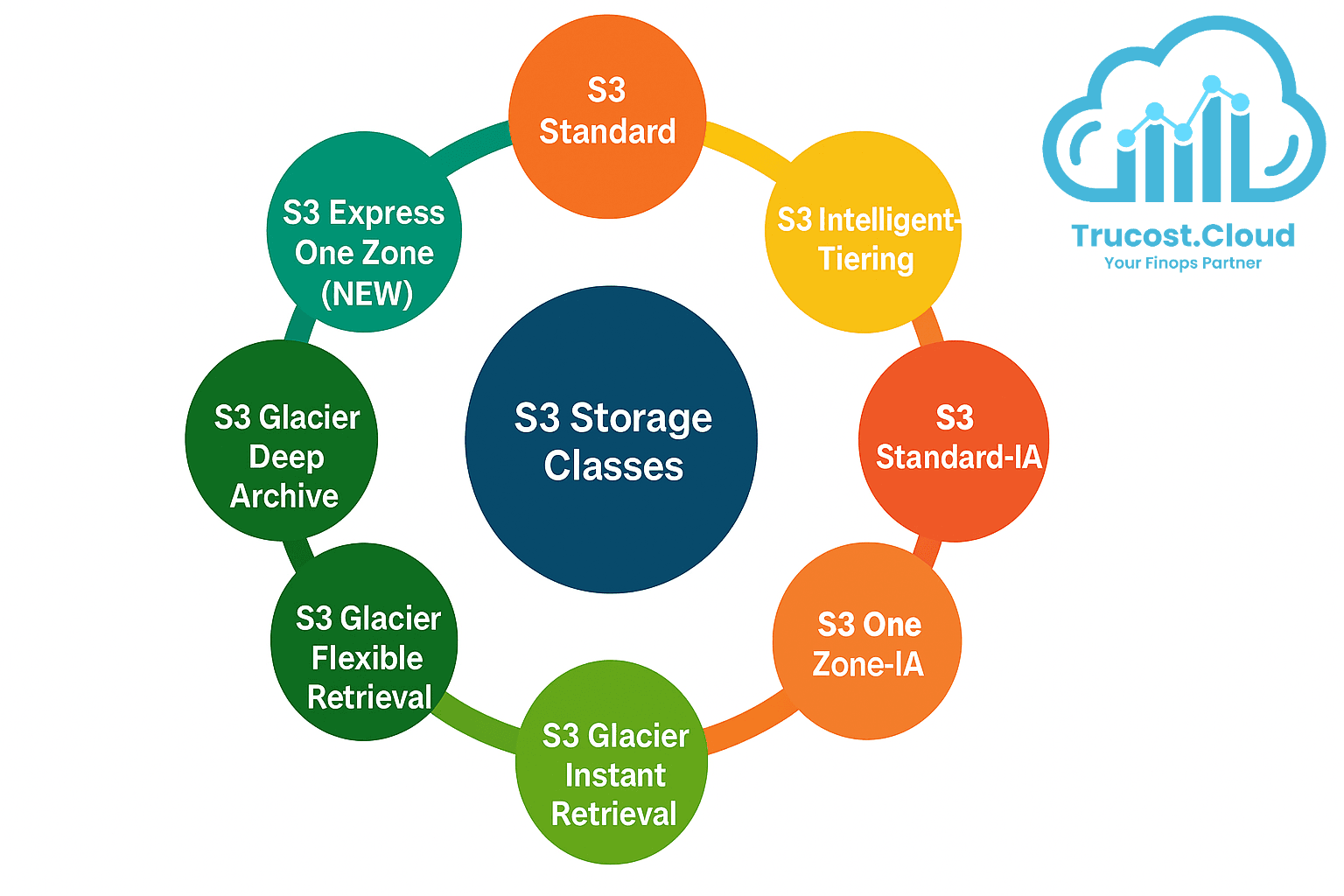
Storage Class | Description | Ideal Use Case | Retrieval Fee | Retrieval Time |
S3 Standard | High durability and low latency for frequently accessed data. | Active data, websites, mobile apps, and content delivery. | None | Milliseconds (low latency) |
S3 Intelligent-Tiering | Automatically shifts data between frequent and infrequent access tiers, with optional Archive and Deep Archive tiers for long-term cost optimization. | Ideal for unknown or changing access patterns. | None for frequent/infrequent tiers; fees apply for Archive/Deep Archive retrieval. | Milliseconds (frequent/infrequent), minutes–hours (Archive/Deep Archive) |
S3 Standard-IA | Lower-cost storage for infrequently accessed data with high durability. | Backups, disaster recovery, long-term storage with occasional access. | Charged per GB retrieved. | Milliseconds |
S3 One Zone-IA | Functions like Standard-IA, but stores data in a single Availability Zone, offering lower costs with reduced redundancy. | Secondary backups or easily reproducible data. | Charged per GB retrieved. | Milliseconds |
S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval | Low-cost archival storage with instant data access. | Long-lived data that requires immediate retrieval. | Low retrieval fee per GB. | Milliseconds |
S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval | Low-cost archive with multiple retrieval options (Expedited, Standard, Bulk). | Compliance archives, disaster recovery backups. | Low retrieval fee per GB. | 3–5 min (Expedited) · 5–12 hrs (Standard/Bulk) |
S3 Glacier Deep Archive | Lowest-cost storage option for rarely accessed, long-term data. | Digital preservation, regulatory or compliance archives. | Low retrieval fee per GB. | 12 hrs (Standard) · 48 hrs (Bulk) |
S3 Express One Zone (NEW) | Ultra-fast single-AZ storage designed for high-performance workloads. | Real-time analytics, AI/ML training, data-intensive applications. | Low retrieval fee per GB. | Milliseconds (ultra-low latency) |
💡 TruCost.Cloud Tip:
For unpredictable access patterns, S3 Intelligent-Tiering is often the best default—it automatically moves data between tiers, saving cost without performance trade-offs.
S3 Lifecycle Management
As data ages, its access frequency often decreases. To optimize costs automatically, S3 provides Lifecycle Policies.
Example of Lifecycle Policies.
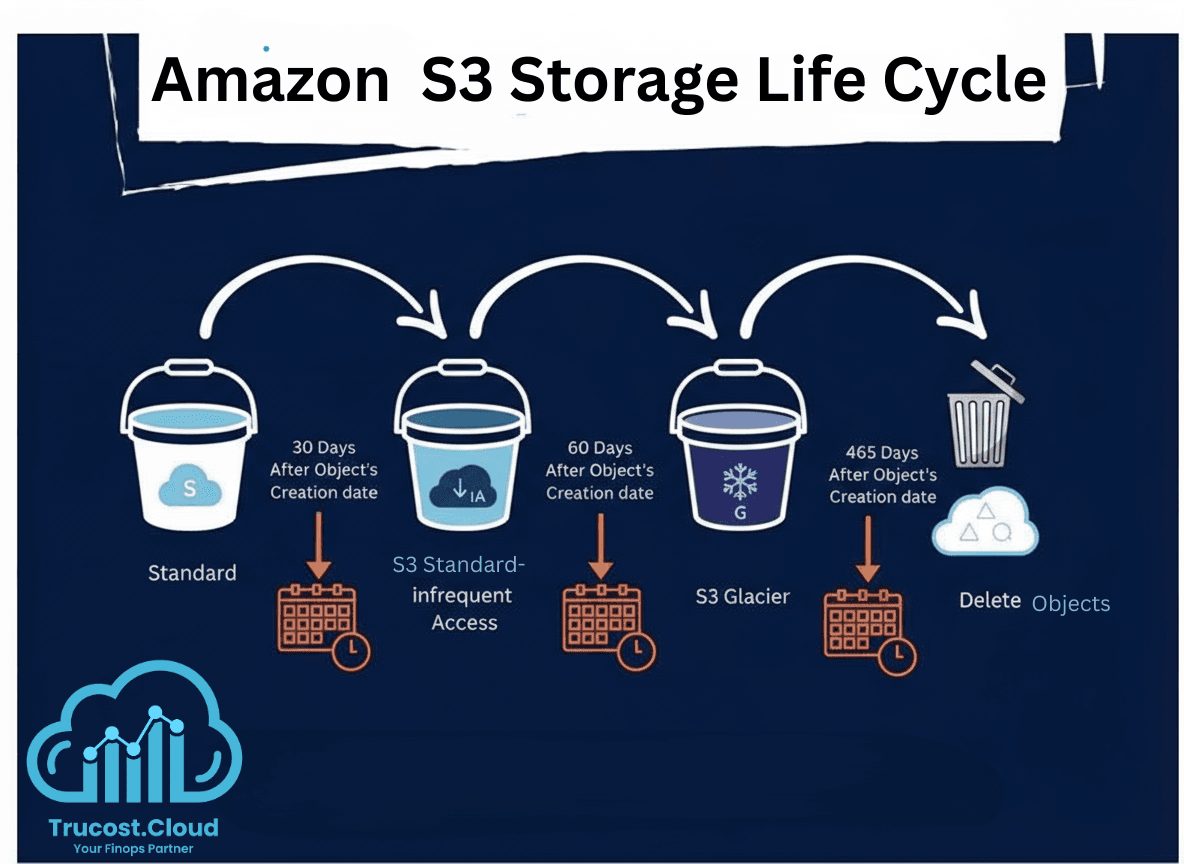
Lifecycle rules let you:
- Transition objects between storage classes (e.g., Standard → Glacier)
- Expire (delete) objects after a certain time
- Clean up incomplete multipart uploads
Example: Amazon S3 Lifecycle Policy
You can automate data transitions between storage classes using S3 Lifecycle rules.
For example:
- Move to S3 Standard-IA after 30 days (for less frequently accessed data)
- Move to S3 Glacier Deep Archive after 180 days (for long-term archival)
- Permanently delete objects after 3 years
This kind of lifecycle policy helps you automatically optimize storage costs over time, ensuring that older or rarely accessed data moves to cheaper storage classes without manual intervention.
Note:
- You can customize days, transitions, and expiration based on your data retention policy.
- Lifecycle rules can be applied at the bucket level or to specific prefixes/tags.
These rules are managed via the AWS Console, CLI, or JSON configuration.
Sample JSON:
{
“Rules”: [
{
“ID”: “ArchiveOldData”,
“Status”: “Enabled”,
“Filter”: { “Prefix”: “logs/” },
“Transitions”: [
{ “Days”: 30, “StorageClass”: “STANDARD_IA” },
{ “Days”: 180, “StorageClass”: “GLACIER_DEEP_ARCHIVE” }
],
“Expiration”: { “Days”: 1095 }
}
]
}
Security Features in S3
Security is a core principle of S3. It provides multiple layers of protection:
1. Access Control
- Bucket Policies
- IAM Policies
- Access Control Lists (ACLs)
2. Encryption
- Server-side encryption (SSE-S3, SSE-KMS, SSE-C)
- Client-side encryption
3. Object Lock
Prevents deletion or modification of data for compliance (e.g., WORM – Write Once Read Many).
4. Logging and Auditing
- S3 Access Logs
- AWS CloudTrail to monitor API calls and detect unusual activity
Common Use Cases of Amazon S3
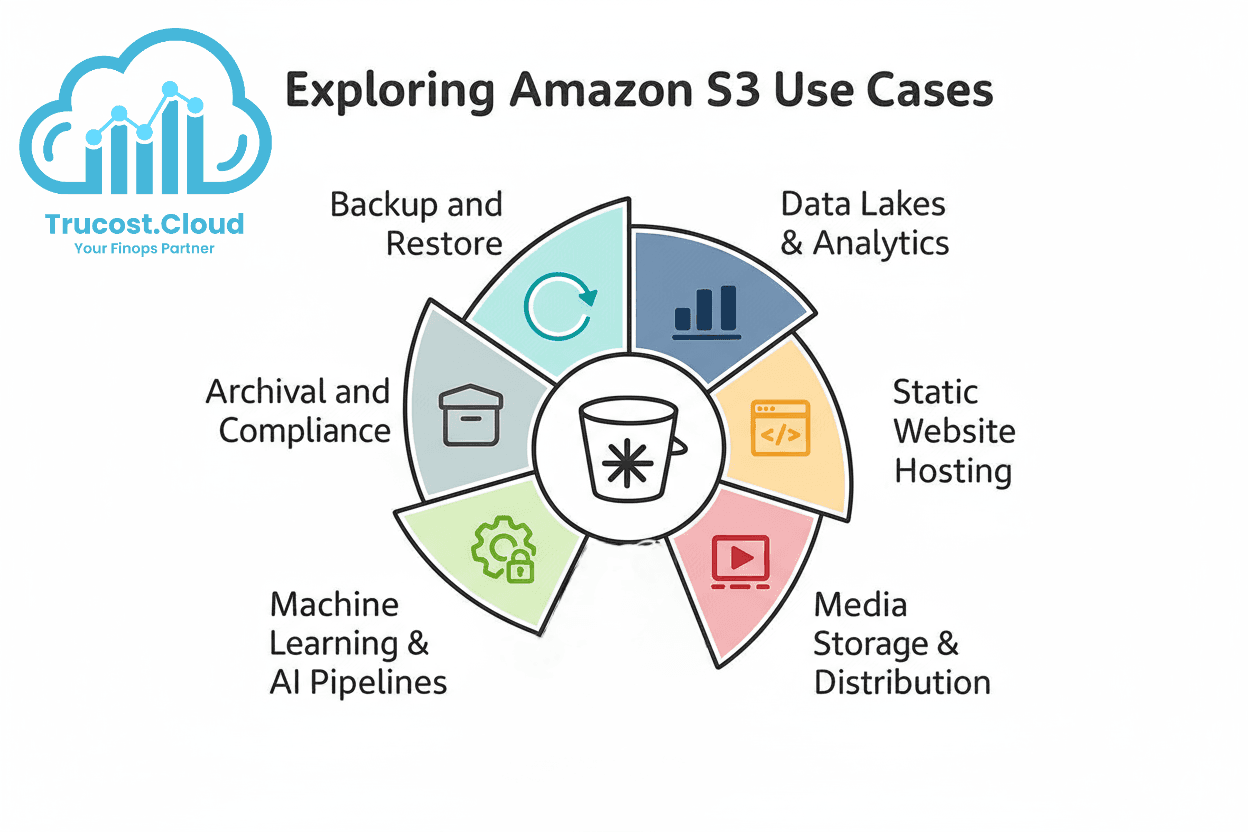
1. Backup and Restore:
Secure and durable backups for databases, servers, and applications.
2. Data Lakes & Analytics:
Store raw, structured, or unstructured data for analysis with Athena, Redshift, or EMR.
3.Static Website Hosting:
Host static content directly (HTML, CSS, JS) without a web server.
4. Media Storage & Distribution:
Store and stream media files integrated with Amazon CloudFront.
5. Machine Learning & AI Pipelines:
Store large training datasets accessible to SageMaker or other ML tools.
6. Archival and Compliance:
Use Glacier classes for long-term retention and regulatory requirements.
Best Practices for S3 Optimization
- Enable Versioning: Protect data from accidental overwrites or deletions.
- Use Lifecycle Policies: Automate cost optimization over time.
- Enable MFA Delete: Add an extra layer of protection for critical buckets.
- Encrypt Everything: Use SSE-KMS for compliance-grade encryption.
- Use S3 Intelligent-Tiering: Let AWS optimize your storage costs dynamically.
- Enable Logging & Monitoring: Track usage and anomalies with CloudWatch and CloudTrail.
- Review Access Regularly: Ensure least-privilege access for users and applications.
- Use Object Lock for Immutable Data: Essential for compliance or audit data.
Conclusion
Amazon S3 remains one of the most powerful and reliable storage services ever built. Its versatility, security, and cost-effectiveness make it suitable for everything from personal backups to petabyte-scale enterprise data lakes.
By understanding what Amazon S3 is, why it’s used, how it works, and how lifecycle policies help manage cost and efficiency, organizations can unlock its full potential—balancing performance, resilience, and financial efficiency.
At TruCost.Cloud, we help businesses make the most of Amazon S3 through data lifecycle optimization, storage class automation, and cost visibility—ensuring every byte of data is stored efficiently and every dollar spent delivers value.
Whether you’re storing a few gigabytes or several petabytes, Amazon S3 scales with your needs, and with TruCost.Cloud’s FinOps expertise, your data will always remain available, secure, and cost-optimized.
Amazon S3 FAQs
1. What is Amazon S3?
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) is a secure, highly durable, and fully scalable object storage service provided by AWS. It allows you to store and retrieve any amount of data from anywhere, supporting applications like backups, data lakes, static websites, and analytics.
2. How does Amazon S3 work?
Amazon S3 stores data as objects within buckets. Each object has a unique key (name), metadata, and the actual data. Buckets are top-level containers with configurable permissions, versioning, logging, and lifecycle rules. You can access S3 data via the AWS Console, CLI, SDKs, or pre-signed URLs.
3. What are S3 storage classes and which one should I use?
Amazon S3 provides multiple storage classes to balance cost and performance:
- S3 Standard – Frequently accessed data, low latency, no retrieval fee.
- S3 Intelligent-Tiering – Auto-moves data between frequent and infrequent tiers, cost-efficient for unknown access patterns.
- S3 Standard-IA & One Zone-IA – Infrequently accessed data with lower cost.
- S3 Glacier & Deep Archive – Long-term archival storage at minimal cost.
💡 Tip: Use Intelligent-Tiering for unpredictable access patterns to save costs automatically.
4. What is S3 lifecycle management?
S3 Lifecycle Management allows automated transitioning of objects between storage classes and expiration of old objects. For example:
- Move objects to Standard-IA after 30 days.
- Move to Glacier Deep Archive after 180 days.
- Permanently delete after 3 years.
This helps optimize storage costs without manual intervention.
5. How durable and reliable is Amazon S3?
Amazon S3 is designed for 99.999999999% (11 nines) durability and 99.99% availability. Your data is automatically replicated across multiple devices and facilities in a region, protecting against hardware failures and outages.
6. How secure is data in Amazon S3?
S3 provides multiple layers of security:
- Encryption: SSE-S3, SSE-KMS, SSE-C, and client-side encryption.
- Access Control: IAM roles, Bucket Policies, ACLs.
- Object Lock: Prevents deletion or modification (WORM compliance).
- Logging & Auditing: S3 access logs and AWS CloudTrail for activity monitoring.
It also complies with HIPAA, PCI-DSS, FedRAMP, and GDPR standards.
7. Can I host a website on Amazon S3?
Yes. Amazon S3 can host static websites (HTML, CSS, JS) directly without a server. When combined with Amazon CloudFront, it provides global content delivery with low latency and high availability.
8. What is S3 versioning?
S3 versioning allows you to maintain multiple versions of an object. This prevents accidental deletions or overwrites and is essential for backups and audit trails. Versioning can be enabled at the bucket level.
9. What is the difference between S3 Standard-IA and One Zone-IA?
- Standard-IA: Stores data across multiple Availability Zones (AZs) for high durability.
- One Zone-IA: Stores data in a single AZ, cheaper but less resilient.
Use One Zone-IA for secondary backups or easily reproducible data.
10. How can I optimize S3 costs?
- Enable Lifecycle Policies to transition infrequent data to cheaper storage classes.
- Use S3 Intelligent-Tiering for unpredictable access patterns.
- Enable versioning and MFA Delete for data protection without unnecessary storage.
- Regularly review access logs and delete obsolete data.
11. What is cross-region replication (CRR) in S3?
CRR automatically replicates objects across AWS regions, providing geographical redundancy, faster access for global users, and compliance with data residency requirements. Same-Region Replication (SRR) replicates data within the same region for high availability.
12. How large can an object be in S3?
Each S3 object can be up to 5 TB in size. Multipart uploads are recommended for files larger than 100 MB for efficient upload and reliability.
13. Can S3 integrate with analytics and AI/ML services?
Yes, S3 integrates seamlessly with:
- Amazon Athena – Query data without moving it.
- Amazon Redshift & AWS Glue – ETL and analytics.
- Amazon SageMaker – Machine learning pipelines.
- CloudFront – Content delivery.
This makes S3 a central hub for modern data-driven applications.
14. What are the common use cases for Amazon S3?
- Backup & Restore: Databases, servers, applications.
- Data Lakes & Analytics: Structured/unstructured data for big data analysis.
- Static Website Hosting: Directly serve static content.
- Media Storage & Distribution: Video, images, streaming.
- ML/AI Pipelines: Large datasets for training and inference.
- Archival & Compliance: Long-term storage using Glacier classes.
15. How do I monitor S3 usage and access?
- Enable S3 Access Logs for request-level logging.
- Use AWS CloudTrail for auditing API calls.
- Leverage Amazon CloudWatch to track usage metrics and set alerts for unusual activity.
16. Is Amazon S3 cost-effective for long-term storage?
Yes. Using Glacier or Deep Archive storage classes with lifecycle policies can drastically reduce costs for infrequently accessed or long-term data while maintaining durability and compliance.
17. Can S3 store structured and unstructured data?
Absolutely. S3 can store any data format—images, videos, text, logs, databases, or backups—making it ideal for data lakes and large-scale analytics projects.










