As cloud-native environments become increasingly complex, understanding and allocating Kubernetes costs accurately is critical for FinOps and engineering teams. Amazon Web Services (AWS) has now made that easier by enabling Kubernetes label integration in split cost allocation data for Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS).
With this powerful enhancement, organizations can now import Kubernetes labels as cost allocation tags into AWS Cost and Usage Reports (CUR). This means teams can directly map Kubernetes workloads — down to pod-level details — to their respective business units, teams, or applications.
The result? Better cost visibility, more accurate chargebacks, and smarter cloud spending decisions.
At TruCost.Cloud, we believe this update is a game-changer for teams looking to strengthen their FinOps and cloud cost management practices on AWS.
What Is Split Cost Allocation Data in Amazon EKS?
Split cost allocation data provides granular cost and usage visibility for container workloads running on Amazon ECS and Amazon EKS.
For EKS specifically, AWS automatically includes system metadata like:
- aws:eks:cluster-name
- aws:eks:namespace
- aws:eks:pod-name
These predefined fields let you track basic pod-level costs. However, with the latest update, you can now import custom Kubernetes labels into the same reports — extending cost visibility into custom attributes, such as:
- Team ownership
- Application name
- Business unit or cost center
- Environment (e.g., dev, test, prod)
This enhancement allows you to customize cost attribution to perfectly align with your organizational and financial reporting structure.
Why Kubernetes Labels Matter for Cost Allocation
Kubernetes labels are simple key-value pairs used to describe and categorize resources like pods, services, and deployments. They’re essential for managing configurations, scaling automation, and now — with this AWS feature — cost allocation.
When imported as user-defined cost allocation tags, Kubernetes labels connect infrastructure usage to business context. This enables organizations to:
- Attribute costs to specific applications, teams, or projects
- Measure total cost of ownership (TCO) per workload
- Align budgets with actual cloud usage patterns
- Improve accountability through data-driven FinOps reporting
By linking Kubernetes metadata with cost data, you get a single source of truth for both technical and financial decision-making.
Difference Between AWS Resource Tags and Kubernetes Labels
Feature | AWS Resource Tags | Kubernetes Labels |
Purpose | Identify and organize AWS resources (EC2, S3, RDS, EKS, etc.) for cost allocation, automation, and access control. | Identify and organize Kubernetes objects (Pods, Nodes, Services, Deployments, Namespaces, etc.) for grouping, scheduling, and monitoring. |
Scope | Operates at the AWS infrastructure level; applies to AWS-managed resources. | Operates at the Kubernetes cluster level; applies to objects within the cluster. |
Visibility | Visible in AWS Console, Cost Explorer, Cost & Usage Reports (CUR), Billing, and IAM policies. | Visible within Kubernetes via kubectl, EKS console, or cluster monitoring tools. |
Use Case | Cost tracking, access control, automation with AWS services (e.g., Lambda, CloudFormation, Cost Explorer). | Workload grouping, service discovery, scheduling, and cost allocation at the pod/service level. |
Structure | Key-value pairs (up to 50 per resource). Example: Environment=Production, Team=DevOps. | Key-value pairs (recommended format: app=frontend, env=prod). |
Propagation | Tags applied to AWS resources (like EC2, EKS, S3) do not automatically propagate into Kubernetes workloads (Pods, Deployments, etc.). You’d need manual mapping or automation to sync them. | Labels applied to Kubernetes objects do not automatically sync back to AWS resources. For example, a label on a Pod won’t show up as a tag on the underlying EC2 instance or EBS volume. |
Integration (via EKS) | With Split Cost Allocation Data, Kubernetes labels can be imported as AWS cost allocation tags for billing and cost visibility. | Labels become part of AWS cost data once imported as cost allocation tags, enabling cross-layer cost visibility. |
Benefits of Using AWS Resource Tags
- Cost Allocation and Reporting
- Tagging resources by Project, Environment, or Owner allows you to break down AWS bills easily.
- You can enable Cost Allocation Tags in the AWS Billing console for detailed reporting.
- Access Management
- Use tags with IAM policies to control access — e.g., only allow users to modify resources tagged with Environment=Dev.
- Automation
- Automate tasks like cleanup, backups, or shutdown of non-prod resources using AWS Lambda + Tag filters.
- Security and Compliance
- Enforce required tags using AWS Config Rules or Service Control Policies (SCPs).
- Visibility Across Accounts
- Centralized tagging makes it easier to monitor usage across multiple AWS accounts via AWS Organizations.
Benefits of Using Kubernetes Labels
- Granular Cost Tracking
- Labels help you attribute resource usage to applications, teams, or namespaces — critical for EKS cost allocation.
- Workload Management
- Kubernetes uses labels to select and group objects (e.g., deploy all pods with app=frontend).
- Scalability and Scheduling
- Labels guide pod placement — e.g., deploy team=ai workloads to GPU-enabled nodes.
- Observability and Monitoring
- Labels make it easier to filter logs and metrics in tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or CloudWatch.
- Cross-Team Collaboration
- Teams can use consistent label schemas to manage large multi-tenant clusters efficiently.
Real-World Use Cases
Here are two practical examples of how teams can apply Kubernetes labels for more accurate and actionable cost allocation.
Use Case 1 – Cost Visibility for Spark Applications in Multi-Tenant EKS Clusters
Consider a shared Amazon EKS cluster running Apache Spark applications on Amazon EMR on EKS. Each Spark pod is automatically labeled with metadata such as:
- spark-app-name = spark_job_a
- spark-app-id = app-12345
Once these labels are imported and activated as cost allocation tags, AWS CUR can show costs per Spark application or aggregate usage across multiple jobs.
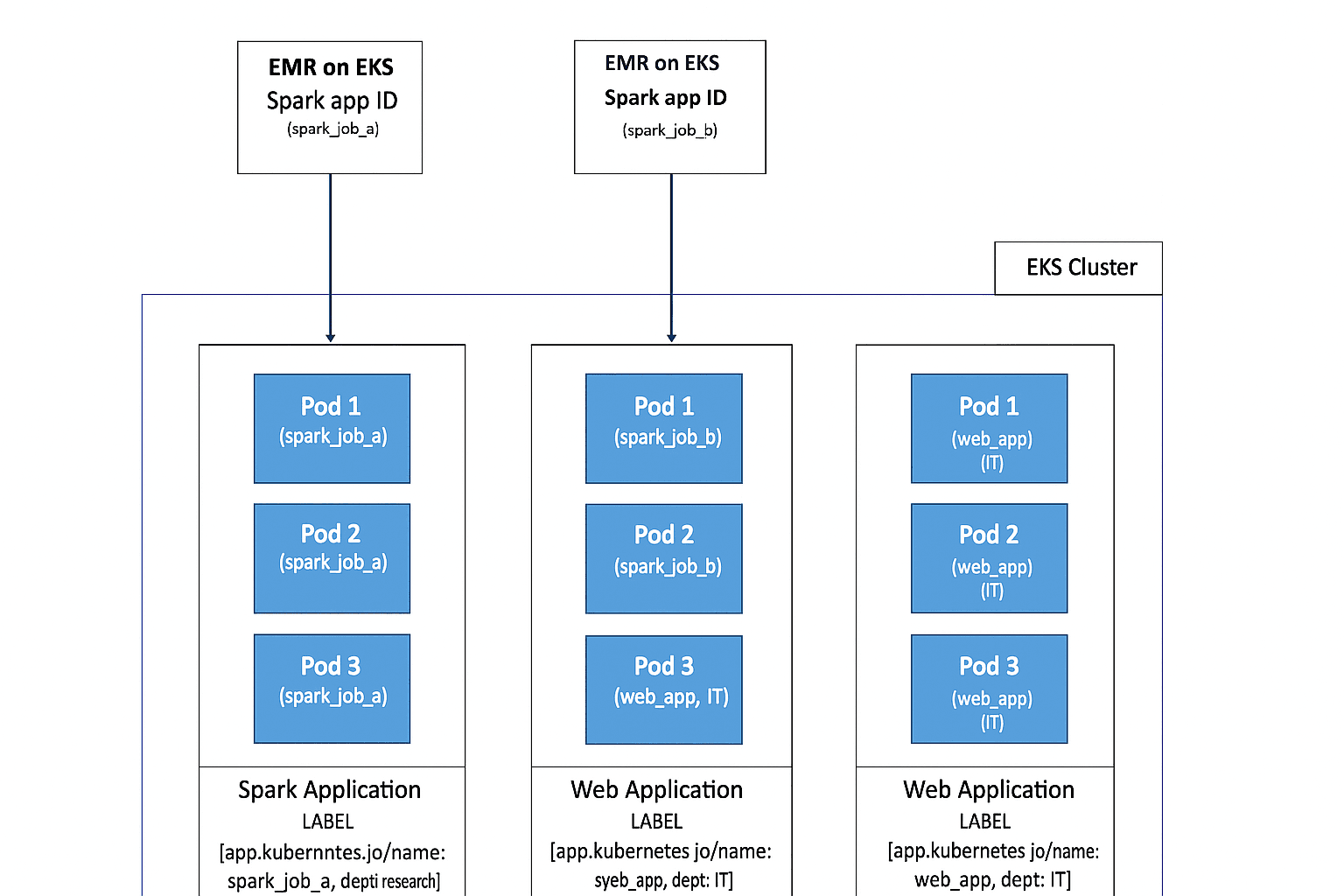
This visibility helps FinOps teams identify which data processing workloads are consuming the most resources, enabling them to optimize cost efficiency while maintaining performance.
Use Case 2 – Calculating Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Across Applications
Most modern applications running on EKS also rely on other AWS services like:
- Amazon RDS for databases
- Amazon S3 for storage
- Amazon OpenSearch Service for analytics
By applying consistent labeling and tagging strategies, such as:
- Kubernetes label: app = web_app
- AWS tag: app = web_app
—you can combine EKS pod costs with AWS service costs to calculate TCO per application.
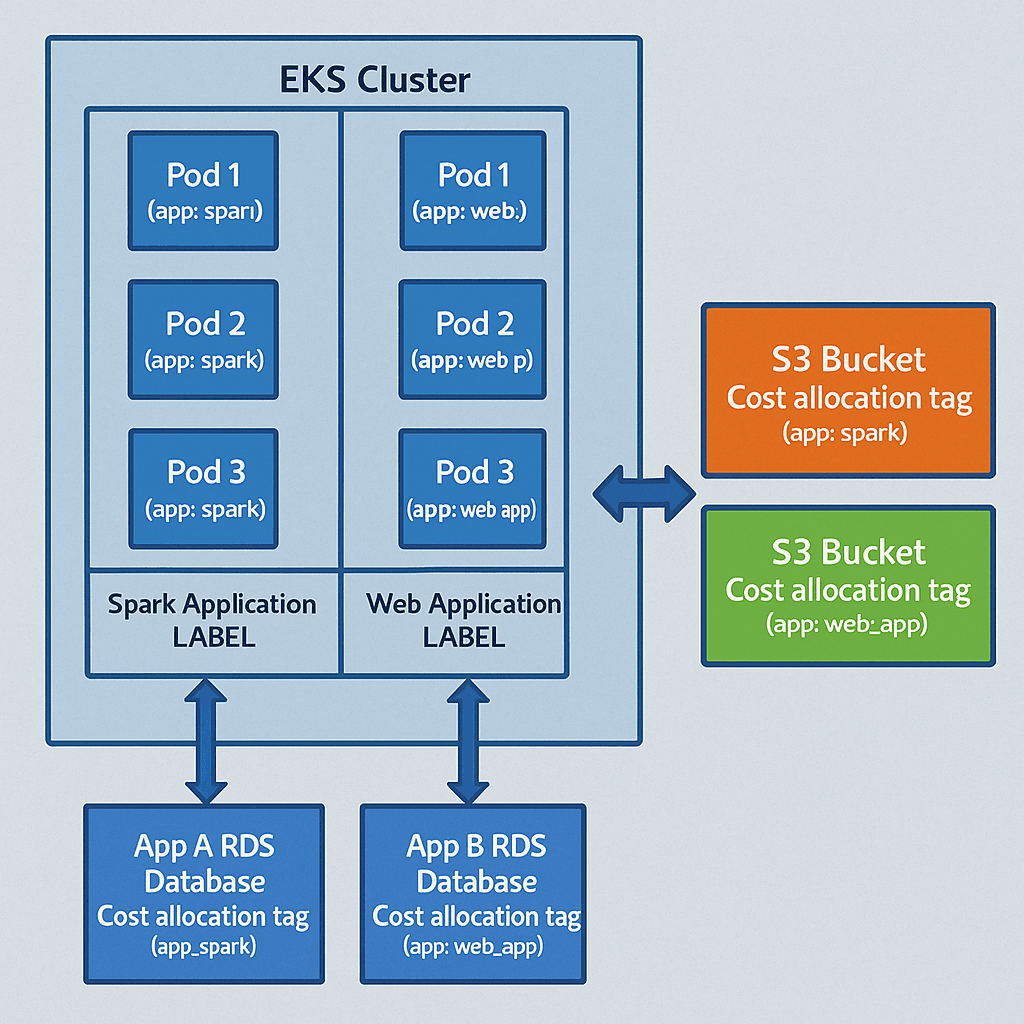
This approach creates a unified financial view of all resources powering each application, helping product owners and FinOps teams maintain full visibility into end-to-end cloud spending.
How to Enable Split Cost Allocation with Kubernetes Labels
Getting started is straightforward. Follow these three simple steps.
Step 1: Enable Split Cost Allocation Data
From your AWS Management Account, open:
➡️ Billing and Cost Management Console → AWS Cost Management Preferences
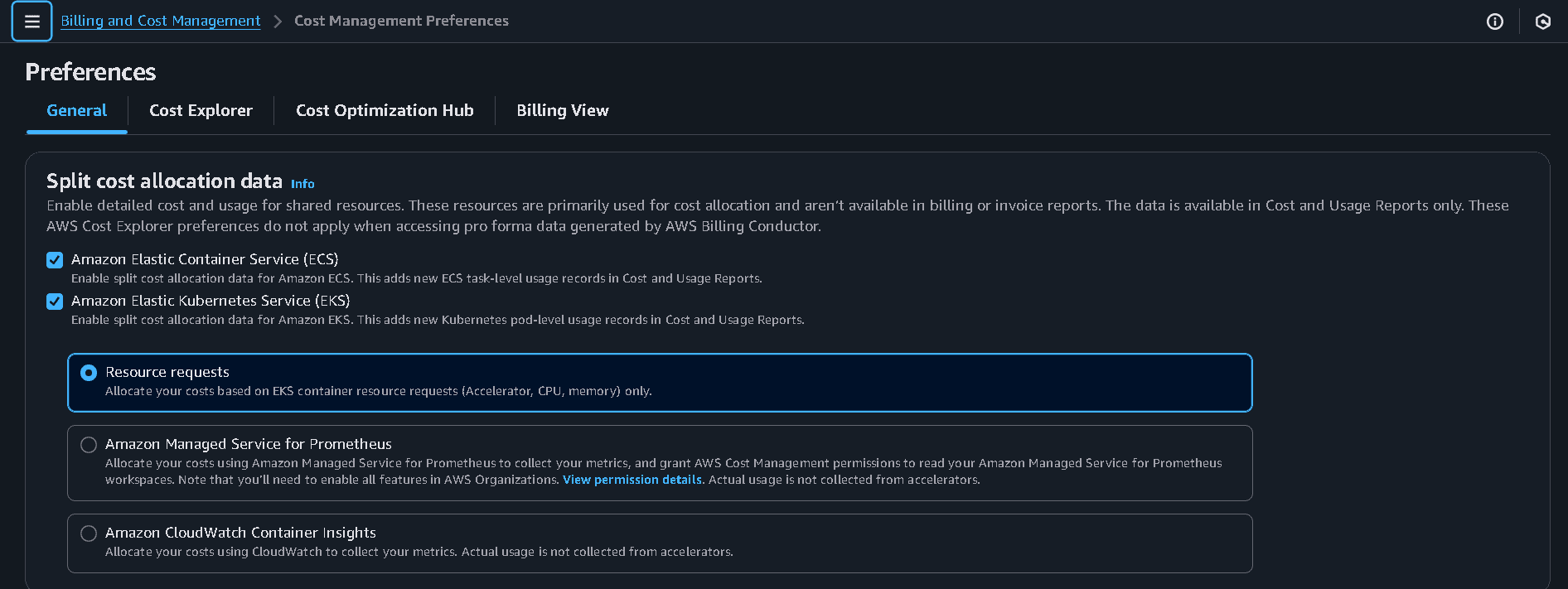
Then:
- Under General Settings, enable Split Cost Allocation Data for Amazon EKS.
- Choose your preferred method for collecting pod-level metrics:
- Resource Requests
- Amazon CloudWatch Container Insights
- Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus
This ensures AWS captures pod-level resource utilization for accurate cost attribution.
Step 2: Activate Cost Allocation Tags
Once Kubernetes labels are imported:
- Go to Cost Allocation Tags in the Billing console.
- Select the Kubernetes labels you want to activate (e.g., app.kubernetes.io/name).
- Click Activate.
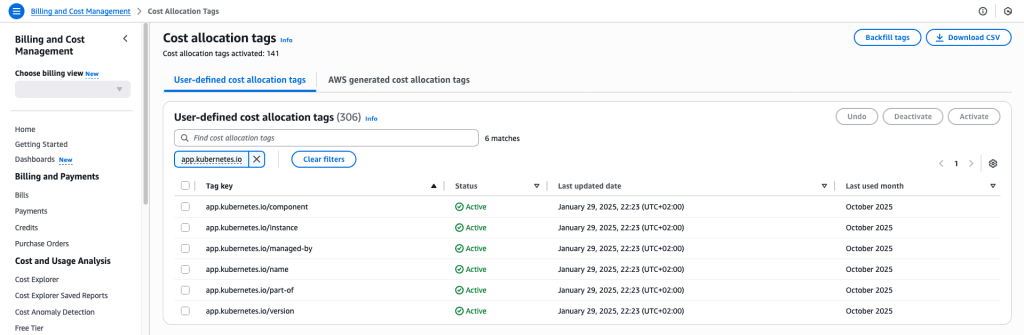
Activated labels then appear as columns in your Cost and Usage Report (CUR), enabling grouping, filtering, and summing by application, team, or environment.
Step 3: Set Up or Edit Your Cost and Usage Report (CUR)
To include split cost allocation data in your CUR:
- Navigate to Billing Console → Data Exports → Cost and Usage Reports.
- Edit an existing report or create a new one.
- Enable the Split Cost Allocation Data
- Include resource IDs and set frequency to hourly for the best detail.
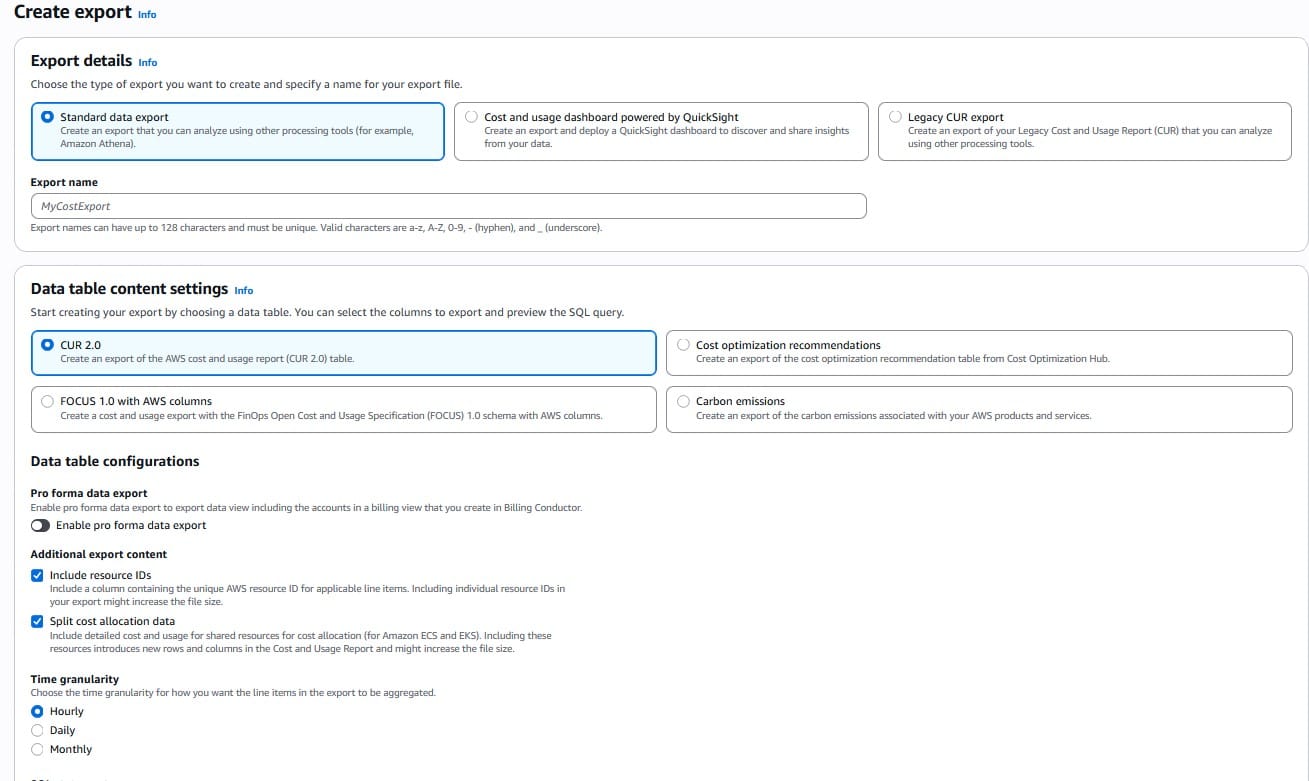
AWS supports both Legacy CUR and CUR 2.0 (recommended).
Your CUR will now include new columns such as:
resourceTags/user:app.kubernetes.io/name
aws:eks:cluster-name
aws:eks:namespace
Learn More
To explore advanced configurations and detailed implementation guidance, check out the official AWS blog: Using Kubernetes Labels to Split and Track Application Costs on Amazon EKS | AWS Cloud Financial Management
Visualizing Costs in Athena and QuickSight
After enabling split cost allocation, you can query your EKS cost data using Amazon Athena or visualize trends with Amazon QuickSight dashboards.
For example, to analyze cost per application, run this Athena query:
SELECT
line_item_usage_account_id,
resourceTags_user_app_kubernetes_io_name AS app_name,
SUM(line_item_unblended_cost) AS total_cost
FROM
cost_and_usage_data
WHERE
product_product_name = ‘Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service’
GROUP BY
line_item_usage_account_id,
resourceTags_user_app_kubernetes_io_name;
This returns cost per Kubernetes application label — ideal for multi-tenant clusters and departmental reporting.
TruCost.Cloud customers can also integrate this data directly into automated FinOps dashboards, combining EKS metrics with broader AWS usage analytics.
Best Practices for Kubernetes Label-Based Cost Allocation
To ensure meaningful, consistent cost insights, follow these best practices recommended by TruCost.Cloud’s FinOps experts:
- Standardize label keys (e.g., app, team, environment, cost_center) across all clusters.
- Automate labeling through CI/CD pipelines or admission controllers.
- Align Kubernetes labels with AWS tags to unify financial visibility.
- Review labels regularly to ensure accuracy and avoid drift.
- Leverage BI tools like QuickSight for real-time executive dashboards.
Business Impact and Benefits
By combining Split Cost Allocation Data with Kubernetes labels, organizations unlock:
✅ Granular visibility into EKS and containerized application costs
✅ Accurate chargeback/showback for departments or teams
✅ Better budgeting and forecasting aligned with actual usage
✅ Improved accountability between engineering and finance
✅ Informed decision-making for cloud cost optimization
This capability bridges the gap between technical utilization and financial reporting, empowering organizations to achieve mature Kubernetes FinOps practices.
Pricing and Availability
There’s no additional charge for enabling Split Cost Allocation Data — only standard Amazon S3 storage costs apply for the incremental CUR data.
The feature is available in all AWS Regions that support Amazon EKS Split Cost Allocation.
Conclusion
The introduction of Kubernetes label-based cost allocation for Amazon EKS represents a major step forward in cloud cost transparency.
By connecting Kubernetes metadata to AWS billing data, businesses can now understand, analyze, and optimize their EKS spending with precision.
At TruCost.Cloud, we help organizations turn this visibility into action — from implementing EKS label-based cost tracking to automating FinOps dashboards and cost anomaly detection across AWS.
Start today by integrating Kubernetes labels into your cost allocation data — and take control of your Kubernetes financial visibility on AWS.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Split Cost Allocation Data in Amazon EKS?
Split Cost Allocation Data provides detailed visibility into how costs are distributed across Kubernetes pods, namespaces, and clusters running on Amazon EKS. It helps teams analyze which workloads or teams are responsible for specific costs within shared EKS environments.
2. How do Kubernetes labels help with AWS cost allocation?
Kubernetes labels are key-value pairs that describe resources. When imported into AWS Cost and Usage Reports (CUR) as cost allocation tags, they allow you to associate AWS spend with specific applications, teams, or environments—improving transparency and accountability in FinOps reporting.
3. What are the benefits of using Kubernetes labels for cost tracking on EKS?
Using Kubernetes labels for cost tracking helps you:
- Attribute costs accurately across workloads
- Improve chargeback and showback models
- Gain insights into total cost of ownership (TCO)
- Make data-driven budgeting and optimization decisions
4.Is there an additional cost for enabling Split Cost Allocation Data in Amazon EKS?
No, AWS does not charge extra for enabling Split Cost Allocation Data. However, you may incur standard Amazon S3 storage costs for the additional data stored in your Cost and Usage Reports (CUR).
5. Can I use Amazon Athena or QuickSight to analyze EKS costs?
Yes. Once Split Cost Allocation Data is enabled, you can query EKS cost data using Amazon Athena or visualize it using Amazon QuickSight dashboards. This allows you to monitor costs per application, team, or namespace in near real-time.
6. How do I import Kubernetes labels into AWS Cost and Usage Reports (CUR)?
You can import Kubernetes labels as user-defined cost allocation tags. After enabling Split Cost Allocation Data in your AWS Billing Console, go to Cost Allocation Tags, activate your desired labels (e.g., app.kubernetes.io/name), and include them in your CUR export settings.
7. What are best practices for labeling Kubernetes workloads for cost allocation?
Follow these best practices for consistent results:
- Use standardized label keys such as app, team, environment, and cost_center.
- Automate labeling in CI/CD pipelines or Kubernetes admission controllers.
- Align Kubernetes labels with AWS resource tags.
- Regularly audit label accuracy and consistency.
8. What AWS services support Split Cost Allocation Data besides EKS?
Split Cost Allocation Data is supported by both Amazon ECS and Amazon EKS, enabling cost transparency for containerized workloads across AWS-managed container services.
9. How can FinOps teams use Kubernetes labels to optimize AWS spending?
FinOps teams can use Kubernetes labels to connect technical metrics with financial outcomes. By analyzing CUR data by label, they can identify high-cost workloads, optimize resource allocation, and implement accurate showback and chargeback models across departments.
10. How can TruCost.Cloud help with Kubernetes cost management?
TruCost.Cloud specializes in AWS FinOps automation, cost optimization, and visibility solutions. Our experts help implement EKS label-based cost allocation, integrate with Athena and QuickSight, and build automated FinOps dashboards that provide actionable insights into containerized workloads.










