In the dynamic world of cloud computing, businesses constantly seek scalable, reliable, and cost-effective ways to distribute traffic and ensure high availability. Optimizing Elastic Load Balancer (ELB), a fully managed service offered by AWS, is one of the core components that helps achieve these goals. However, while ELB provides substantial operational benefits, it can become expensive if not optimized properly.
In this blog post, we’ll explore how to maximize the benefits of Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) and keep costs under control, so you can maintain application performance without breaking your budget.

What is an Elastic Load Balancer?
An Elastic Load Balancer intelligently distributes incoming application requests across multiple targets—such as Amazon EC2 instances, containers, IP addresses, and Lambda functions—spanning one or more Availability Zones to enhance fault tolerance and scalability.ELB scales as traffic changes over time and comes in three main types:
- Application Load Balancer (ALB) is designed specifically for web traffic—it excels at managing HTTP and HTTPS requests and offers advanced routing capabilities like path-based and host-based routing to direct users exactly where they need to go.
- Network Load Balancer (NLB) is engineered for blazing speed and massive scale. It effortlessly handles millions of connections with ultra-low latency, making it the go-to choice for TCP, UDP, or TLS traffic where performance is non-negotiable.
- Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB) specializes in simplifying the deployment and scaling of third-party virtual appliances like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and deep packet inspection tools—taking the complexity out of managing these critical security layers.
Key Benefits of ELB
- High Availability and Fault Tolerance
ELB automatically balances traffic across multiple Availability Zones, minimizing the impact of zone failures and ensuring that your applications remain available.
- Scalability
With auto-scaling integrations, ELB dynamically adjusts to changing traffic patterns. This ensures smooth performance even during sudden spikes in user demand.
- Secure and Compliant
You can offload SSL/TLS termination to ELB and use built-in authentication, AWS WAF, and security policies. This reduces the strain on backend servers while supporting adherence to regulatory compliance.
- Health Monitoring
Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) continuously monitors the health of your instances and ensures that traffic is only sent to those that are up and running smoothly. This self-healing behavior enhances uptime and reliability.
- Advanced Routing
ALB supports host-based, path-based, and header-based routing, enabling microservices architecture, blue/green deployments, and A/B testing with ease.
Cost Components of ELB
ELB pricing depends on the type you use and has two primary cost components:
- Load Balancer Hours – The number of hours or partial hours your ELB is running.
- LCU Used – The amount of data processed by the ELB in GBs.
Additional costs may apply if you’re using AWS PrivateLink, cross-zone load balancing, or custom SSL certificates.
Strategies to Maximize Value and Minimize Costs
Here are actionable strategies to optimize your ELB usage while keeping expenses low:
- Choose the Right ELB Type
Choosing the appropriate Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) for your specific needs is essential because:
- Use ALB for web applications with complex routing.
- Choose NLB for latency-sensitive, TCP-based apps.
- Opt for GWLB only if you need to deploy third-party virtual appliances.
Choosing the wrong load balancer can lead to higher operational costs and underutilized features.
- Enable Cross-Zone Load Balancing Judiciously
Cross-zone load balancing improves traffic distribution but comes with additional data transfer costs. Evaluate your app’s architecture before enabling this feature. If traffic is not evenly distributed across zones, it might be more cost-efficient to disable it.
- Consolidate Load Balancers
Deploying too many load balancers increases costs. Group microservices under fewer ALBs using path-based or host-based routing. This minimizes the quantity of load balancers required and streamlines management processes.
- Use Target Groups Efficiently
Instead of using multiple load balancers, leverage target groups to organize your backends by service or version. You can assign multiple services under one ALB using different target groups, minimizing ELB count and cost.
- Monitor and Optimize with CloudWatch
Use Amazon CloudWatch to track ELB metrics like request count, latency, and unhealthy hosts. Set alarms to detect anomalies and right-size or terminate underutilized load balancers.
- Leverage Auto Scaling
Combine Elastic Load Balancers with Auto Scaling Groups to automatically scale backend instances in response to traffic demands, ensuring both cost savings and peak performance without unnecessary resource overuse.
- Idle Load Balancer Audit
Take time to regularly review your AWS setup to spot load balancers that are sitting idle or barely being used—these quiet culprits can drain your budget without you even noticing. Decommissioning unused ELBs can immediately reduce costs.
- Integrate with AWS WAF Smartly
Using AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF) on ALBs provides security at the edge but incurs additional charges. Optimize WAF rules to ensure you’re only filtering what matters most, avoiding unnecessary processing costs.
Real-World Cost Optimization Example
Imagine a SaaS platform initially running 10 microservices, each behind its own ALB https://calculator.aws/#/createCalculator/ElasticLoadBalancing. Monthly ELB cost =
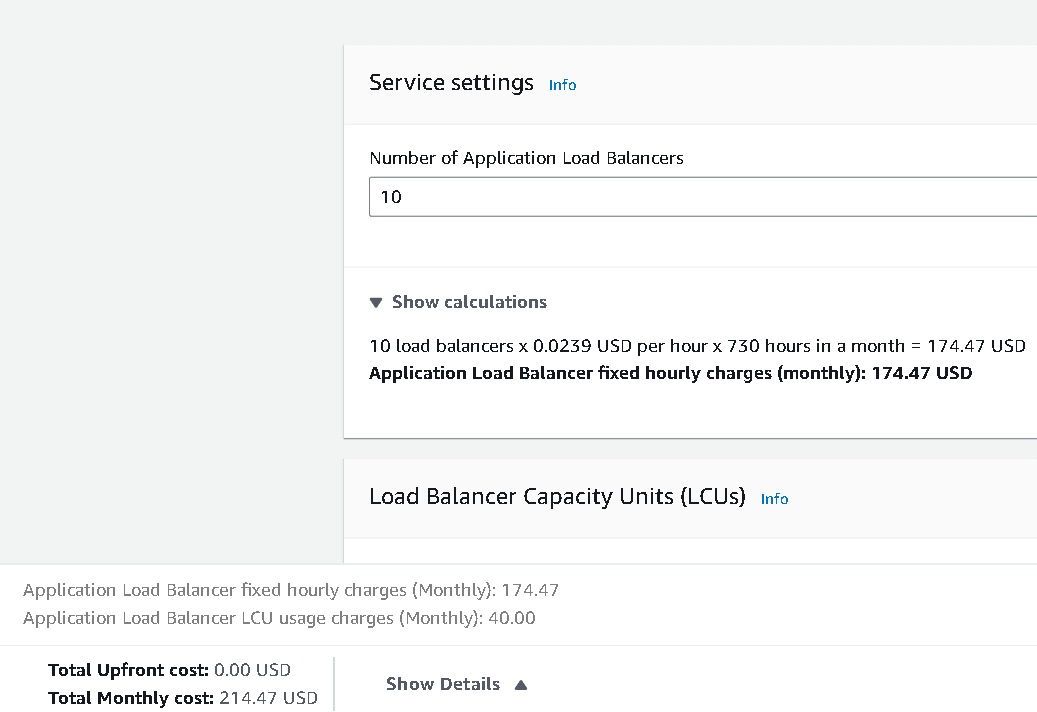
Imagine a SaaS platform initially running 10 microservices, each behind its own ALB. Monthly ELB cost =
- 10 load balancers x 0.0239 USD per hour x 730 hours in a month = 174.47 USD
- LCU Used: 10 load balancers x 0.68493 LCUs x 0.008 LCU price per hour x 730 hours per month = 40.00 USD
- Total Monthly cost: 214.47 USD
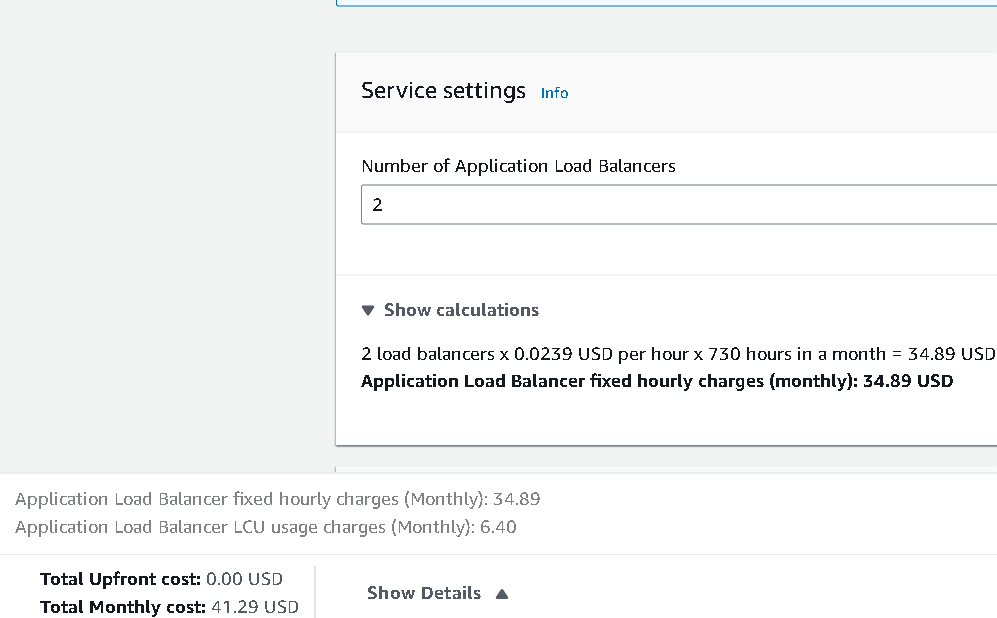
By consolidating services into 2 ALBs using path-based routing, and reducing idle data processing, the cost drops to:
- 2 load balancers x 0.0239 USD per hour x 730 hours in a month = 34.89 USD
While this might seem small, it’s a cost worth monitoring—especially as your environment grows.
- LCU Used: 2 load balancers x 0.547944 LCUs x 0.008 LCU price per hour x 730 hours per month = 6.40 USD
- Total Monthly Cost: 41.29 USD
That’s almost 80% savings, with improved architecture manageability.
Tools and Services to Assist You
Here are some AWS tools to aid in cost and performance optimization:
- AWS Trusted Advisor acts like a built-in cloud consultant—it automatically flags underutilized Elastic Load Balancers (ELBs) and highlights chances to save money by shutting down or rightsizing unused resources.
- AWS Cost Explorer lets you explore your spending in detail, helping you understand exactly how much your Elastic Load Balancers (ELBs) are costing—and where you might save. With intuitive visuals and filtering options, you can spot trends, identify spikes, and even forecast future ELB expenses—so you’re never caught off guard when the bill arrives.
- AWS Savings Plans – Not specific to ELB, but consider for EC2 workloads paired with ELB to reduce overall infrastructure cost.
Final Thoughts
Elastic Load Balancer is a robust and adaptable service designed to boost your application’s performance and ensure it stays reliable under varying traffic loads. But like any AWS service, its cost can spiral if not actively managed.
By choosing the right ELB type, consolidating resources, and actively monitoring usage, you can enjoy all the benefits of ELB while keeping your AWS bill in check. Start with a small audit today and scale your optimizations as your infrastructure evolves.
Get Expert Help from TruCost.Cloud
Need guidance on AWS cost allocation, tagging compliance, or cost showback? The specialists at TruCost.Cloud are here to support you. We’ll work with you to implement smart tagging strategies, maintain compliance, and uncover opportunities to reduce cloud spend. Start today and take charge of your cloud spending with confidence.










